At Nucleus IVF, Pune, Dr. Pritam Prakash Sulakhe guides couples through the important differences between fresh and frozen embryo transfers, helping them understand the benefits, timing, success rates, and suitability of each option so they can make informed and confident decisions on their fertility journey.
He carefully evaluates individual medical history, hormone levels, and embryo quality before recommending the most appropriate approach. By personalizing treatment plans, he aims to maximize implantation success while ensuring the safest possible outcome for both mother and baby. This patient-centered approach empowers couples with clarity, confidence, and realistic expectations throughout their IVF treatment.
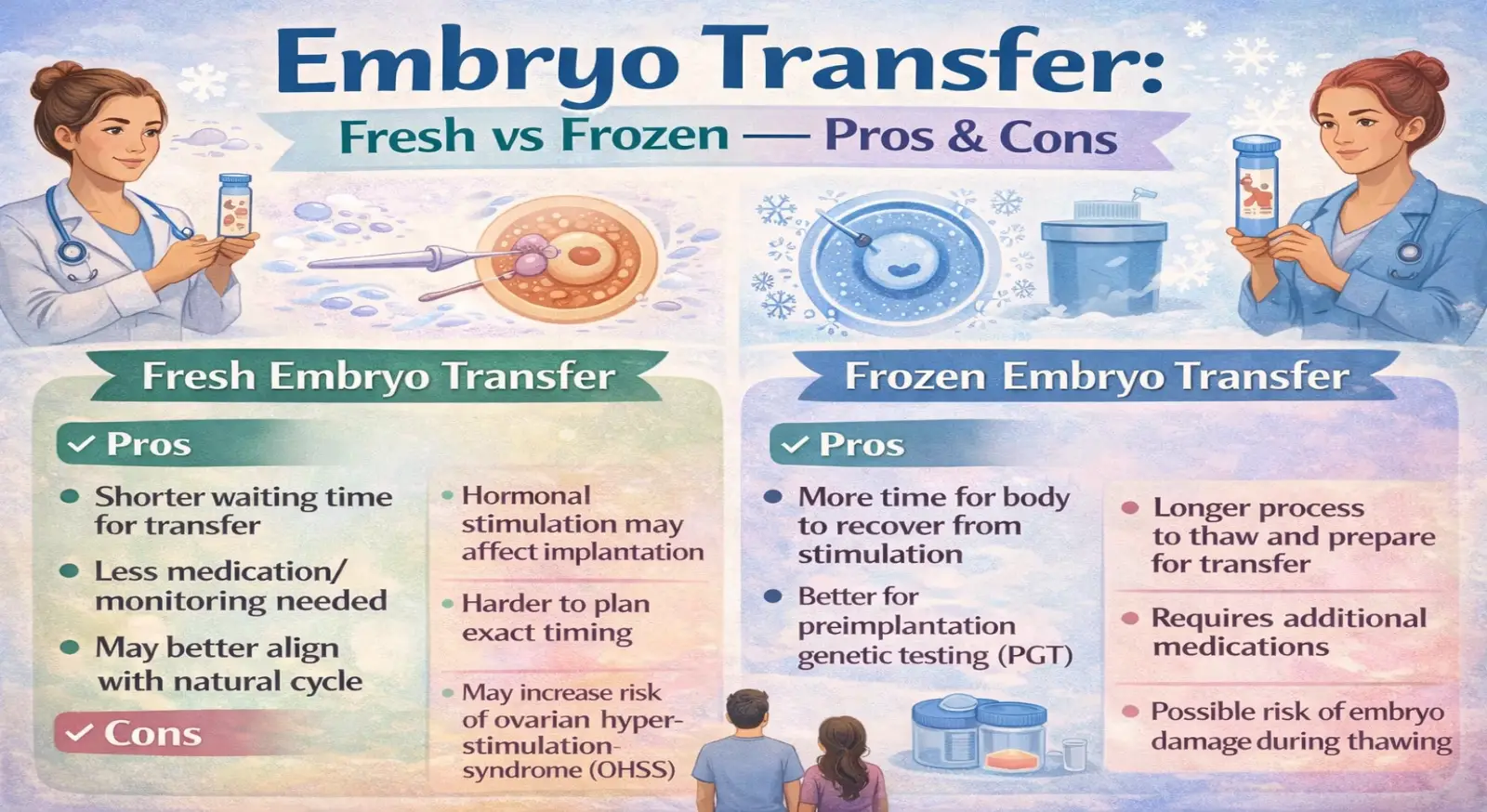
What Is Fresh Embryo Transfer?
Fresh embryo transfer occurs within the same IVF cycle after egg retrieval. Once the eggs are collected and fertilized in the laboratory, the resulting embryo is transferred into the uterus typically within 3 to 5 days.
This approach reduces waiting time and allows couples to move forward without delay. For many patients, the shorter timeline feels emotionally reassuring because the transfer happens immediately after embryo development.
Advantages of Fresh Transfer
• Shorter overall treatment timeline
• Lower immediate cost (no freezing or storage charges)
• Faster emotional closure for that cycle
However, fresh transfer is done during the same cycle in which ovarian stimulation medications are used. These medications increase hormone levels, particularly estrogen, which can sometimes affect the uterine lining and implantation environment.
In some women, especially those who respond strongly to stimulation, the uterus may not be in its most optimal receptive state at that time.
What Is Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET)?
Frozen embryo transfer involves freezing embryos after fertilization and transferring them in a later cycle. The embryos are preserved using advanced freezing techniques, most commonly vitrification.
Vitrification is a rapid freezing method that prevents ice crystal formation, protecting embryo structure and survival rates. Modern vitrification techniques have significantly improved success rates, making frozen embryos just as viable as fresh ones in many cases.
In a frozen cycle, the woman’s body is allowed to return to hormonal balance before transfer. The uterine lining is then prepared naturally or with controlled medication in a separate cycle.
Advantages of Frozen Transfer
• Better uterine environment
• Reduced risk of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
• More flexible scheduling
• Often improved implantation rates in selected patients
By separating ovarian stimulation from embryo transfer, doctors can optimize the uterine lining under more stable hormonal conditions.
Hormonal Environment: Why It Matters
During ovarian stimulation, hormone levels—especially estrogen—can rise significantly. While this helps produce multiple eggs, it may temporarily alter the uterine lining’s receptivity.
In a frozen embryo transfer cycle, the body is not under the influence of stimulation drugs. This often creates a calmer, more natural environment for implantation.
Several studies suggest that in certain groups of patients—such as women with high estrogen levels, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), or risk of OHSS—frozen transfer may provide better outcomes.
Risk of OHSS
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) is a condition that can occur when the ovaries over-respond to stimulation medications. Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to more serious complications.
By freezing embryos and delaying transfer, doctors can significantly reduce the risk of OHSS. This makes frozen transfer particularly beneficial for high responders.
Success Rates: Fresh vs Frozen
Research shows that success rates between fresh and frozen embryo transfers are often comparable. In some cases, frozen embryo transfer may even show slightly higher implantation rates.
However, success depends on several factors:
• Woman’s age
• Hormone levels during stimulation
• Embryo quality
• Uterine lining thickness
• Previous IVF history
• Underlying medical conditions
For younger women with normal hormone levels and good uterine response, fresh transfer may be equally effective.
For women with high hormone levels or previous implantation failure, frozen transfer may offer improved outcomes.
Emotional and Practical Considerations
Emotionally, many couples prefer fresh transfer because it shortens the waiting period. After egg retrieval and embryo formation, moving directly to transfer can feel more hopeful and less stressful.
On the other hand, frozen transfer offers more flexibility. It allows time for:
• Genetic testing if required
• Recovery from stimulation
• Better scheduling
• Improved physical and emotional preparation
Some couples also appreciate the option to plan the transfer around work or family commitments.
Cost Differences
Fresh transfer may involve lower immediate cost because it avoids freezing and storage fees. However, if a fresh transfer fails due to poor uterine receptivity, the overall treatment cost may increase.
Frozen transfer involves additional costs for freezing and storage, but it may reduce the risk of cycle cancellation or complications in certain patients.
A personalized discussion with a fertility specialist helps determine the most cost-effective approach in the long term.
When Is Fresh Transfer Recommended?
Fresh transfer may be recommended when:
• Hormone levels are stable
• Uterine lining looks optimal
• There is low risk of OHSS
• Embryo quality is good
• No medical complications are present
In such cases, proceeding within the same cycle can be efficient and effective.
When Is Frozen Transfer Preferred?
Frozen embryo transfer is often preferred when:
• Estrogen levels are very high
• There is risk of OHSS
• Uterine lining needs optimization
• Genetic testing is planned
• Previous fresh cycle failed
Each situation is unique, and medical guidance is essential.
Personalized Decision-Making
There is no universal “better” option. The decision between fresh and frozen embryo transfer depends on individual medical factors, hormone response, and overall reproductive health.
A tailored approach ensures the highest chances of success while maintaining safety.
Final Thoughts
Both fresh and frozen embryo transfers are scientifically advanced and highly effective IVF techniques. With modern laboratory methods and improved cryopreservation technology, frozen embryos now show excellent survival and implantation rates.
The key lies in selecting the right approach for the right patient at the right time.If you are undergoing IVF treatment, discuss your hormone levels, embryo quality, and medical history with your fertility specialist. An informed decision can significantly improve your chances of achieving a healthy pregnancy.
Choosing between fresh and frozen embryo transfer is not just about timing — it is about optimizing success while prioritizing safety and long-term outcomes.
Dr. Pritam Prakash Sulakhe
Dr. Pritam Prakash Sulakhe
author
Dr. Pritam Prakash Sulakhe has completed his MBBS from B J Government Medical College , Pune which is one of the top medical College in India. He continued his post-graduation as DGO at same institute. After that he opted for Diplomat Of national Board In Obstetrics and Gynecology from Kerala Institute Of Medical Sciences Trivandrum, which is one of the most prestigious institute from South India.


